Basic provisions of Vietnamese law regarding consolidation and absorption-type mergers
2023/06/01
- US CPA
- Masaya Sakai
1. Definitions and characteristics of corporate mergers and acquisitions
1.1 Definitions
Both consolidation and absorption-type mergers are considered a form of corporate restructuring under Vietnam Enterprise Law1 and a type of economic concentration under Competition Law.2 A consolidation-type merger is “a merger in which two or more businesses terminate their business activities or cease to exist by having a newly established company transfer all of their assets, rights, obligations, and legal interests”.3 Once the registration of a consolidation-type merger is completed, all of the companies that are parties to the merger (the merged companies) disappear, and a single new company (the merging company) is born which inherits all of their rights and obligations.4
A merger is defined as “the termination of the business activities of one or more businesses or the disappearance of such businesses by having another business succeed all of its assets, rights, obligations and legal interests”.5 In an absorption-type merger, the company that transfers all of its assets, rights, obligations, and legitimate interests (the merging company) among the multiple companies involved in the merger is dissolved upon completion of the transfer registration to the company that accepts these assets (the accepting company).6
In addition, under the Enterprise Law, it is stated that either of these can naturally be implemented through a contract between the parties, but in order for this to be valid in relations with the authorities, new business registration procedures and business registration change procedures must be carried out in accordance with the Investment Law. Therefore, when a foreign-owned company merges with a Vietnamese-owned company, there may be cases where it is unable to inherit business licenses that are subject to restrictions on foreign capital entry.
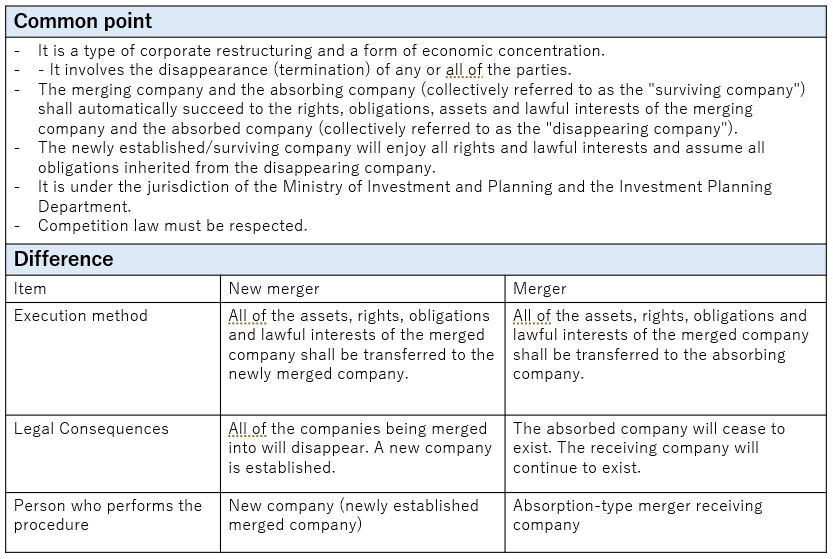
1.2 Characteristics (Similarities and Differences)
The similarities and differences between new establishment mergers and absorption mergers are summarized in the table below.
2. Overview of procedures for consolidation and absorption-type mergers
There are many similarities between the procedures for establishment-type mergers and absorption-type mergers. The outline is as follows:7
Step 1: In the case of a consolidation-type merger, the merged companies will negotiate to prepare a consolidation agreement and draft articles of incorporation for the consolidating company. In the case of an absorption-type merger, a draft absorption-type merger agreement and articles of incorporation of the receiving company are prepared.
Main points of the merger and consolidation agreement
– Name and head office address of the newly merged company (accepting company)
– Name and head office address of the newly merged company (the company being absorbed into)
– Procedures and conditions for consolidation (absorption)
– Draft implementation plan for using labor
– The deadline, procedures and conditions for the transfer of assets of the merged company (absorbed company) and the transfer of its equity, stocks and bonds to the new merged company (accepting company)
– Deadline for consolidation (absorption)
Step 2: In a consolidation, each merging company adopts a consolidation agreement and proposed articles of incorporation of the merging company. In an absorption-type merger, the accepting company and the merging company each adopt a merger agreement and the accepting company’s proposed articles of incorporation. The convening of the meeting or general assembly for adoption, the method of adoption and the terms of adoption shall be in accordance with the provisions of the Enterprise Law depending on the company type.
Step 3: The merger/consolidation agreement must be sent to all creditors and notified to employees within 15 days of its adoption.
Step 4: The new joint venture company applies for new business registration. Since this is a company incorporation, there is no set application deadline. In the case of an absorption-type merger, the accepting company must submit an application for amendment to the business registration if there are any changes to the business activities carried out after the merger, or a notice to that effect if there are no changes to the business activities, to the competent investment bureau. In either case, the application must be submitted within 10 days.
3. Conclusion
This report describes the provisions regarding new establishment mergers and absorption-type mergers under current law. The legal provisions are simple, but when it comes to actually carrying out a new establishment merger or absorption-type merger, the competent authorities may conduct more in-depth examinations and confirmations, and may instruct the submission of additional documents, just as with other procedures. When carrying out a new establishment or absorption-type merger, it is important to check the latest regulations and official letters in advance, and to plan and execute the transaction carefully while confirming and coordinating with the competent authorities.
1Chapter 9 of the Enterprises Act 2020 (the “Enterprises Act”)
2Article 29(1) of the Competition Act 2018 (hereinafter referred to as the “Competition Act”).
3Article 29, paragraph 3 of the Competition Act
4Article 200, paragraph 1 of the Enterprise Law
5Article 29, paragraph 2 of the Competition Act
6Article 201, paragraph 1 of the Enterprise Law
7Article 200, paragraph 2 and Article 201, paragraph 2 of the Enterprise Law
*This article was translated by Yarakuzen.



